
Recognizing Deficiencies and surpluses with Your Cannabis Plant
In this article we will dive deeper into the most common shortages and surpluses with cannabis plants. How do you know when the soil is depleted and your plant is hungry? Are the leaves hanging down, or are they full of brown spots? Typical questions that require more explanation. Th at’s why we do our best to guide you through the world of leaf problems in cannabis plants in this article.
The Disc of Eighteen
Does your cannabis plant look discolored or completely unhealthy? It may be your cannabis plant has a nutritional deficiency. As we described in ‘Leaf problems with cannabis plants Part 1: How to prevent problems’, cannabis plants need more than just water and light. Cannabis plants grow relatively quickly when we compare them with other plants. However, due to this growth spurt, they also need more nutrition in a short time, compared to other plants. Still, what nutrition you give cannabis plants? Meet the Disc of Eighteen.
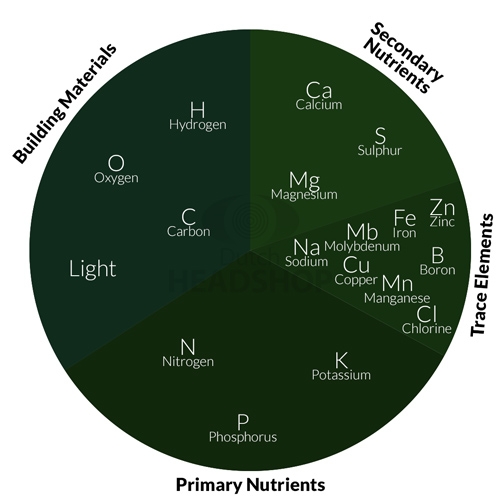
Growth conditions
In the purple pie point we can observe light, hydrogen, oxygen and carbon. These conditions ensure the plant creates the material that it allows to grow. Nutrients are taken up by the cannabis plant in the form of sunlight, water and carbon dioxide (CO2). Through photosynthesis, CO2 and water are converted into oxygen and glucose. Glucose forms the structure of the plant, though it's not enough for a plant to stay healthy.
Trace elements, Primary and Secondary Nutrients
Nutrition for cannabis plants is available in small 'edible’ chunks. These chunks contain the other fourteen elements a cannabis plant needs. This allows the plant to create luscious buds for tasty cannabis with THC, CBD and terpenes. These fourteen elements can be divided into three categories:
- Primary nutrients; nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
- Secondary elements; calcium, sulfur and magnesium.
- Trace elements such as zinc, sodium and manganese.
The Life Cycle of the Cannabis Plant
We discussed in ‘Leaf problems with cannabis plants Part 1: How to prevent problems’ that the cannabis plant needs nutrition in every phase of life. Actually, it can only germinate without nutrition, provided the seed has sufficient germination power. Young plants (seedlings) can use some extras. Especially if you want them to grow quickly and become strong. In the growth phase, a plant mainly needs nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium: the primary nutrients. As the flowering progresses, the demand for trace elements increases.
Simple advice: provide nutrition when you water your plants, except if you have a very rich nutrient base.
Leaf Problems in relation to the Disc of Eighteen
It is now clear which nutrients a cannabis plant actually needs, so we will continue to discuss what happens when a cannabis plant experiences shortages. The most common leaf problems can be divided in responses to shortages in the area of ??primary nutrients, secondary nutrients and trace elements.
We will look at the signals the leaves give for each element. In the picture on the left, you can see a healthy cannabis leaf and the specific leaf problem on the right.
1. Shortage of Primary Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium
Nitrogen
As far as nutrition is concerned, a shortage of nitrogen is most easily recognized. The cannabis leaf is a lot lighter and even uniform yellow at the tips. In case of a nitrogen deficiency, it is important you notice the leaves feel low-weight. Do the leaves feel heavy? You have given too much water. The cannabis leaves becomes heavy and uniform yellow from the tips.

Nitrogen shortage
Symptoms of nitrogen deficiency are (chronological order):
- The lower leaves turn yellow.
- The cannabis leaf loses its shine.
- The cannabis leaf first becomes yellow at the tips, after which it slowly pulls to the heart of the leaf.
- Leaves lose their green color and start curling.
- Leaves starting to fall off.
- Cannabis plants remain smaller and have smaller leaves.
- The cannabis plant flowers too early and has a low yield.
Phosphorus
Recognizing a phosphorus deficiency is somewhat more difficult compared to a nitrogen deficiency. This is because some symptoms resemble other shortages or surpluses. Still, one characteristic really stands out: at an early stage the cannabis leaves turn blue-green.

Phosphorus deficiency
Symptoms of a phosphorus deficiency are (chronological order):
- The petioles color purple.
- The growth rate of the cannabis plant is decreasing.
- The well-known leaf problem: dark spots (from purple to black) at the ends of the lowest cannabis leaves.
- Cannabis leaves with serious deficiencies turn dark purple, twist, curl and eventually fall off the cannabis plant.
- The cannabis plant is seriously weakened and therefore susceptible to diseases and vermin.
Potassium
Your cannabis plant has rusty or burnt edges and yellow to orange leaves full of dark spots? This is clear indication of a potassium deficiency. Another striking element with a potassium deficiency is the fact cannabis plant grows strangely. The cannabis plant gets ramifications in places where it shouldn't. It looks like a genetic abnormality.

Potassium deficiency
Symptoms of a potassium deficiency are (chronological order):
- Older weed leaves turn pale.
- The ends of the leaves turn rusty and look burnt.
- The stem of the cannabis plant gets weak, thin and brittle.
- The amount of branches may increase.
- Flowering decreases and the cannabis plant looks deformed.
2. Shortage of Secondary Elements: Calcium, Magnesium and Sulfur
The secondary nutrients are important for the overall health of the plant. In addition, it is important you do not give too much of these nutrients, otherwise the absorption of other substances will be blocked.
Calcium

Calcium deficiency
A calcium deficiency can be recognized as follows:
- The lower weed leaves twist and bend.
- A small cannabis plant is produced, with a reduced yield.
- The development of flowers goes slowly.
- Yellow-brown, irregular spots on the cannabis leaves and edges.
- The roots can die off at the ends.
Magnesium

Magnesium deficiency
Your cannabis plant has a magnesium deficiency? Then leaf problems of the cannabis plant only occur after four to six weeks. Before that you won't see from the outside the cannabis plant is going crazy for magnesium. The symptoms:
- The cannabis leaf turns yellow between the leaf veins.
- The older leaves have rusty brown spots (especially) at the ends.
- The cannabis plant gives an overall ill impression.
- Older weed leaves dry out, and eventually fall off.

Magnesium surplus
An excess of magnesium is also a recognizable leaf problem with cannabis plants. The symptoms:
- The leaves turn deep, dark green.
- The cannabis plant remains small, as the intake of other nutrients is blocked.
Sulfur

Sulfur deficiency
The leaf problems of sulfur deficiencies are also clearly distinguishable. The symptoms:
- Young cannabis leaves stay small and turn bright green to yellow.
- After a certain amount of time, the leaf veins also turn yellow and eventually dry out.
- The tips of the weed leaves burn, get darker and bend downwards.
- The trunk becomes hard and wooden with purple stripes, especially if there is an overall nutrition shortage.
- Flower buds grow slowly and are weak, so the cannabis plant's yield is minimal.
3. Shortage of trace elements: Iron and Zinc
There is a whole list of trace elements, and we cannot clearly distinguish the shortages of each one of them. The symptoms are too similar. However, two leaf problems are most noticeable with regard to a shortage of trace elements: iron and zinc.
Iron

Iron deficiency
When your cannabis plant asks for iron, the leaves turn yellow from the heart to the edges. You can especially notice it by the color between the leaf veins. The symptoms (chronological order):
- Turning yellow from the heart, starting with young leaves.
- Larger leaves will also turn yellow later on.
- The leaves develop black, dead spots and eventually fall off.
- The growth of the cannabis plant decreases, and the yield goes down quickly.
Zinc

Zinc deficiency
Too much zinc is uncommon. Leaf problems in cannabis plants due to a shortage of zinc, do however occur. Yellowing leaves with burnt dots are a visible result. The symptoms:
- In case of a zinc deficiency, young leaves turn yellow, get thin and curl.
- Young weed leaves are wrinkled.
- For the trunk at the end it is difficulty to grow taller, which means the outgrowth often is limited to a single place.
- The tips of the leaves discolor and burn.
- The space between the branches decreases. The cannabis plant remains small, and there is virtually no yield because the flowers do not grow much larger than a small bud.
Too Much Nutrition? What is Enough?
Perhaps after seeing these leaf problems with cannabis plants, you think: "If I keep providing nutrition, it should all be fine." Unfortunately, this is not the case. Cannabis plants are very sensitive. An excess or shortage of nutrients is never the solution. See the picture below.

If you keep providing nutrition, the plant will not perform better. The ends will burn and the entire plant will die off.
Therefore the question is, how much nutrition do you provide a cannabis plan so it is and remains healthy? Plagron comes with a clear, simple advice: provide nutrition every time you water. The advice applies to both the growth and the flowering phase of the cannabis plant. This ensures your plant gradually receives nutrition, while it will consume it to get tall and strong. The amount of nutrition is always stated on the packaging. Royal Queen Seeds advises to mix 50 to 100 grams of Vertafort organic nutrition with gradual release with 20 liters of earth.
Wait, there is more! Pay attention to Diseases, Fungi and Pests
What we would like to say with this article is that it is important to provide nutrition to your plants. No man will stay healthy on water and dry bread, and the same principle applies to cannabis plants. We hope it will be somewhat easier to recognize leaf problems from your beloved cannabis plant and quickly provide a solution.
However, even when you do your utmost best by satisfying the disc of eighteen, cannabis plants can also provide shelter for annoying tenants. Think, for example, of diseases, pests and fungi. Within a short period of time they can heavily damage the cannabis plant. They just come around. How to deal with this? Can you reduce the chances of this? Read this and much more in: Leaf problems with cannabis plants Part 3: Life-threatening diseases »
