
You experience leaf problems with your cannabis plants? Back to the basics
When your cannabis plant has yellow leaves curling in, it's often difficult to attribute it to a single problem. This makes recognizing leaf problems with cannabis plants hard. Simply put: there can be several problems at the same time. So, let's keep it simple let's get back to the basics; the basic need of cannabis plants. Without these elements your cannabis plant won't grow. If these conditions are fulfilled, it is easier to tackle leaf problems of the cannabis plant effectively.
The basis of a cannabis plant consists several factors, namely:
- Soil
- Water
- pH level
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Light
- Nutrition
1. The Soil
Every plant needs water. However, even more important than water to the cannabis plant, is soil. When growing in soil, an excess of water has to be able to flow away (read: drainage). Therefore, ensure there are holes at the bottom of the pot, or use a smart pot. This helps for preventing multiple problems. For example, the roots cannot rot because of a water surplus.

A fine soil is airy and contains organic matter such as plant remains, fungi and bacteria. If your potting soil looks looks similar to soil shown in the picture, you have a good start.
If the soil in the pot is airy, the roots are able to grow more easily, and it is well oxygenized. Therefore, never stamp the ground. Furthermore, do not add wood chips to the ground for making the mixture more airy. Cannabis does not do well on wood chips.
Outdoors, a sandy loam soil works like a charm. It is rich in nutrients and stimulates natural drainage (water drainage). Loam allows the roots to grow without much resistance.
2. Water
When you are sure soil has enough drainage, you can look at the amount and frequency of watering. You provide plenty of water to your cannabis plant. Provide water until 10 to 20 percent of the given water drips out at the bottom of the pot.
Your cannabis plant has yellow leaves?
Providing too much water to the cannabis plant will causes its leaves to hang. The leave is bent downwards over the entire length by the weight of the water. After a long time, the leaves turn pale yellow. The leave still feels solid.

When providing too much water, the leaves will hang and the leaves of the cannabis plant turn pale yellow.
Too little water
Strangely enough, the leaf also starts hanging when you provide too little water. You can notice the difference when touching it. Dry leaves feel limp, thin and lifeless. Eventually, the leaves of the cannabis plant will hang down completely, lose all resilience and break off. Another consequence of a lack of water is the leaves becomes susceptible to burning. Especially now, the plant becomes extra sensitive to too high temperatures and the placement of lighting, causing the dots to turn brown or even black.

You give your cannabis plant too little water? In no time the cannabis plant collapses like a house of cards. The leaves feel fragile, like thin as paper.
How often do you water your cannabis plant?
Only water your cannabis plants when the soil feels dry. How do you know this? Carefully put your finger into the ground or coconut fiber and in case the soil feels dry up to your first phalanx, it is time to give water. Only provide water when the soil is dry.
Note: water is rarely 'only' water
Watering with tap or rain water is seldom 'simply' water. It also contains minerals. Signs of incorrect water management often look like nutritional deficiencies at first glance. For this reason, it is essential to provide a correct basis for your cannabis plant before you think of a shortage of, for example, nitrogen or phosphorus.
You would like to know more about nutritional deficiencies and surpluses for your cannabis plant? Then read Leaf problems with cannabis plants Part 2: Recognizing deficiencies.
3. The pH value
Acidity is expressed in pH. pH 7 is neutral and everything below is acidic. A pH of 8 to 14 is basic (or alkaline). The ideal pH value of a cannabis plant is just below the neutral acidity. Try to reach a pH of 6 to 7 and the cannabis plant will do fine. The reason is that close to this acidity level, most nutrients are perfectly absorbed.
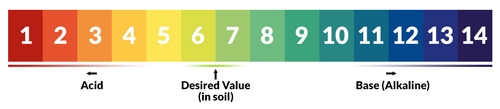
You can best measure the pH value with an appropriate acidity meter. Still, with some experience one can see cannabis leaves change color when the acidity changes. The pH value is then too high (alkaline soil). Nutrition such as Plagron pH min can lower the pH value of the cannabis plant on purpose.
Is the soil too acidic? You can observe that from irreparable burn marks on the cannabis leaves. If you don't intervene, your cannabis plant shall wither under acidic conditions. You need to take action quickly. You can also easily dissolve a too low pH with the correct nutrition of Plagron.
4. The ideal temperature
The ideal temperature for young cannabis plants is between 20 and 25 degrees. Higher temperatures are OK for an adult cannabis plant, but it is important to maintain the temperature as constant as possible. Maintain the temperature at night and your cannabis plant will reward you. Indica-dominant plants are more resistant than the sativa. To ensure high yields, make sure the temperature does not drop below 20 degrees.

A cannabis plant that gets too hot, develops problems in creating beautiful buds.
5. Humidity
The correct relative humidity is preferably quite high during the growing phase. 65 to 70% is really good. Why? The immature plants have not yet developed a good root system and are better able to absorb moisture from the air via the leaves. A mature plant that is not yet in flower can tolerate a lower percentage of moisture. Lower the humidity each week by around 5%, down to a minimum of 40%. Is the plant about to flower? In that case lower the humidity to a value between 40 and a maximum of 50%.
It’s a bit like the ideal temperature in your growing area. Don’t lower the temperature during the growing and early flowering phase to below 21 degrees Celsius. In the final 2 weeks before the harvest, you can lower the overnight temperature by 5-10 degrees compared to the daytime temperature (18-24°C).
Air too humid during flowering?
Quickly take action. Refresh the air. Put your cannabis plant outside in the wind and place a fan indoors. This also strengthens the fibers of the cannabis plant’s stems, so the plant will be able to support the huge flower buds.
6. Light
How much light is sufficient for a cannabis plant? Cannabis plants are doing well in full sun. For autoflowering cannabis seeds, there is no need to take light schedules into account. Simply plant from May to August. With autoflowers, more light also means more yield, but make sure the temperature below the lamp will not rise too high.
Strains that do not flower automatically will usually grow larger. Non-autoflowers, often sold as feminized, have never been crossed with cannabis ruderalis and will therefore start to flower in the sun when days get shorter. The same is true when you put the cannabis plant inside. Only when days get shorter (or when lighting is turned off for more time in the night) your cannabis plant will flower.

You get the best results for starting the flowering when you darken for 12 hours. We call this a 12/12 schedule. During growth, an 18/6 schedule is commonly used. 18 hours of light, 6 hours of darkness.
24 hours of light
On the internet you can read cultivation reports of experiments with 24 hours of light during the growth phase. Take into account that in virtually all successful cases, also CO2 is being added to the grow room. Only autoflowers can be exposed to 24 hours of light without any problems. This regime does not only require more light, but also more nutrients and water. It can result in ten to thirty percent extra yield, but the question is whether the extra investment in energy is worth it.
7. Nutrition
A common beginner's mistake is assuming your plants only need water and light to grow. Cannabis plants also need nutrition to eventually produce weed. Soil naturally contains nutrients the cannabis plant uses during its lifetime. Over time, the soil contains less and less nutrients, until the soil is completely depleted. It is important to provide your cannabis plant with the right nutrients during all the phases of its life.
Cannabis plant has germinated - The Seedlings
Babies consume breast milk, but adults have a much more varied diet. The same principle applies to cannabis plants. The cannabis plant uses different nutrients in each life phase. You used a rich soil when you started planting the cannabis plant? Then this diet is often sufficient for the cannabis plant to grow its first leaves. You can provide your seedlings (the first leaves) with a rich diet with Vita Race from Plagron or soil improver. This ensures your young cannabis plant makes it to the adult phase quickly and healthy. As time passes and the plant grows, your cannabis plant requires more.
Phase of life: Growth
In the growing phase, the cannabis plant uses a lot of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. These elements are also the first to disappear from the soil. Although these elements are the most important, nothing short of 18 elements from three groups are necessary for growing a healthy cannabis plant. By far the most important thing to remember is nitrogen. You can recognize a shortage of nitrogen by its yellow leaves.
The purpose of the plant's growth is to lay the foundation for large buds. Make sure that the level of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium will not drop too much, otherwise your maturing cannabis plant will have a hard time. And you will notice this by a reduced or even failed harvest.

Can you give too much nutrition to your cannabis plant? See the above image for a 'fattened' cannabis plant. The soil has been acidified by a surplus of nutrients, causing the weed leaves to burn.
Phase of life: Flowering
During flowering, the cannabis plant transports glucose and other important nutrients to the flowers. The required nutritional composition changes during flowering. In particular the demand for the nutrients potassium and phosphorus is increasing. Keep in mind though to not forget the secondary nutrients, such as sulfur, magnesium and calcium. Sulfur stimulates the production of terpenes that provide the cannabis plant with taste, aroma and its well-known effect.
You would like to know more about leaf problems with cannabis plants?
We talked about the basic elements of a cannabis plant. First of all, you want to prevent leaf problems in cannabis plants by meeting these basic elements. Nevertheless, practice teaches this is often more difficult then you thought. Probably, you will start reading this article when something is wrong with your cannabis plant (leaf problems).
Our advice? Watch the leaves of your cannabis plant. After all, leaves are a better indicator than they appear at first glance. Deficits are communicated by discoloration and damage to the leaves. In the next article we will dive deeper into the most common shortages with cannabis plants.